As a founder of a SaaS company, you need multiple hats
You spend your morning with the marketing team and noon with the finance department.
It’s a rollercoaster to grow a SaaS business.
You need to acquaint yourself with marketing terminologies and acronyms to communicate swiftly with the marketing team and to better evaluate marketing performance.

1. Annual Recurring Revenue (ARR)
Used for: Finding revenue a SaaS company will generate in the next year based on its active subscriptions.
Formula: (Sum of subscription revenue for the year + recurring revenue from add-ons and upgrades) – revenue lost from cancellations and downgrades
Benchmark: There’s no specific benchmark as ARR is used with other metrics to evaluate SaaS performance.
The expected annual recurring revenue expected from all active subscribers of a SaaS company. It’s used to determine the long-term revenue your app will make. ARR is used for subscription-based pricing models irrespective of billing cycle (weekly, monthly, or annually). It helps you in decision-making and budgeting.
ARR is used with Monthly Recurring Revenue (MRR) for meaningful insights.
2. Average Revenue Per Paying User (ARPPU)
Used for: Analyzing average revenue per paid user of an app to determine profitability, cash flow, and budgeting.
Formula: Total Revenue generated in a specific time period / Total number of paying users in that same time period.
Benchmark: ARPPU must be higher than customer acquisition cost. Benchmark varies across industries as a B2B SaaS might have an ARPPU of $1,000 while a B2C SaaS might have it in the range of $5.
It measures the average revenue your SaaS business generates from a paying subscriber in a specific time period (e.g., monthly or biannual). It’s a financial metric but it’s crucial for marketing as it helps you set a realistic customer acquisition budget.
3. A/B Testing
Used for: Conversion rate optimization
A/B testing (or split testing) is an experiment where two (sometimes more) versions of an element (variable) are shown randomly to the users to identify a winning version that converts better. It’s a test used to improve the conversion rate on marketing pages.
You can use the A/B test to compare two versions of your SaaS pricing page and see which one converts more visitors into customers. It lets you increase the conversion rate across your website by testing different variables subsequently.
4. Attention, Interest, Desire, Action (AIDA)
Used for: Understanding the customer journey and optimizing it for conversions.
AIDA model is a framework that describes the stages of the SaaS sales funnel. A potential customer first gets attention, then develops an interest in your brand and app, it leads to desire, and finally the user takes action and becomes a customer.
It’s used in inbound marketing to attract your target audience to your software by publishing helpful content. That’s how you get the attention of ideal customers.

5. Buyer Persona
Used for: Better understanding of your ideal customers.
A buyer persona (marketing persona, customer persona, or audience persona) is a semi-fictional representation of your ideal customers. It is developed using primary data that you collect from your target audience such as demographics, interests and hobbies, pain points, goals, etc.
Buyer personas help you reach your target audience at the right time and the right touchpoint. This significantly improves marketing campaign targeting.
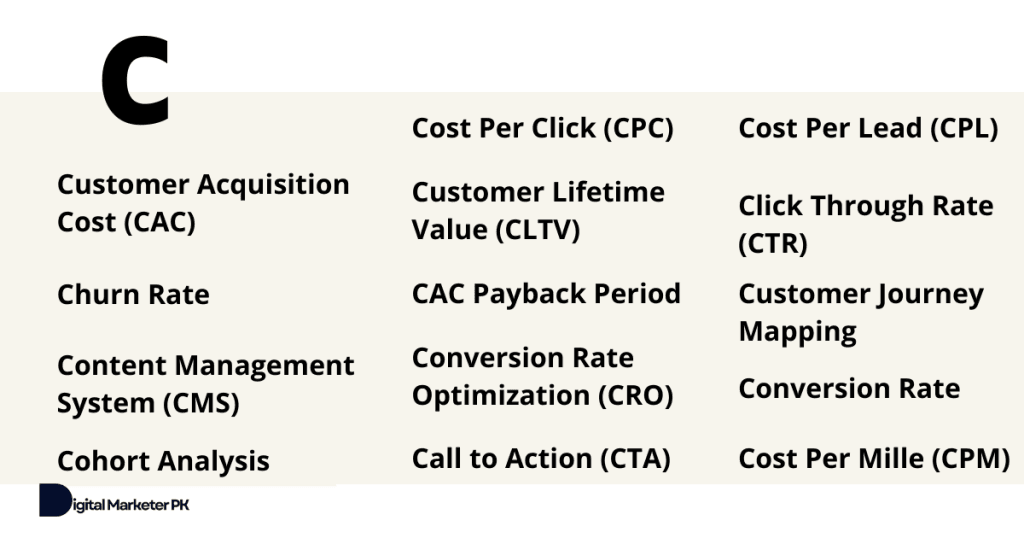
6. Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC)
Used for: Measuring total cost to acquire a customer.
Formula: Total marketing and sales expenses) / Number of new customers acquired (in a specific time period)
Benchmark: CAC should be lower than customer lifetime value (CLTV) to maintain positive cash flow. The general rule is to have a ratio of 3:1.
Customer acquisition cost is the total cost to acquire a new customer for your SaaS business. The cost doesn’t just include marketing spend rather it covers everything end to end. CAC is a variable metric that keeps changing based on your expenses (e.g., annual marketing budget). It needs to be measured for a specific time considering the total costs in that time and total customers acquired in the same duration.
7. Customer Lifetime Value (CLTV)
Used for: Measuring total revenue expected to be generated per customer.
Formula: Customer value x Average customer lifespan
Benchmark: Ideally, CLTV should be higher than CAC and the ratio should be 3:1.
Customer lifetime value (CLV or CLTV) measures the total revenue a SaaS company expects to generate from a single paying customer for a lifetime. It includes all the purchases a customer is expected to make throughout the relationship with your brand.
A clear understanding of CLV helps you set a realistic marketing budget that will keep your business profitable.
8. Churn Rate
Used for: Tracking paying customers who cancel subscriptions in a given period.
Formula: (Customers lost / Total customers at the end of the time period) x 100
Benchmark: The B2B SaaS churn rate should be around 5% annually while for B2C SaaS businesses, the annual churn rate benchmark is between 5-7%.
The churn rate tracks the percentage of paying customers who leave your SaaS company in a specific time period (e.g., month or year). It’s the rate at which your SaaS business loses customers. Churn rate helps you forecast cash inflow, identify issues in your app, and find areas of improvement.
9. CAC Payback Period
Used for: Calculating the time it takes to get back the cost of acquiring a new customer.
Formula: CAC / Average gross margin per customer
Benchmark: The average CAC payback period benchmark for B2C SaaS companies is around 5-6 months while it’s around 12 months for B2B SaaS businesses.
CAC payback period is a critical SaaS metric that measures the time your SaaS brand needs to retrieve the cost you spent on acquiring a new customer. It indicates the efficacy of your customer acquisition strategy. A short CAC payback period is ideal as it indicates that your business starts generating profit from a customer quickly which is a healthy sign.
10. Conversion Rate
Used for: Measure the percentage of visitors who complete a conversion action.
Formula: (Conversions / Total visitors) x 100
Benchmark: SaaS websites have an average conversion rate between 2-5%.
Conversion rate refers to the rate at which your site converts. It measures the percentage of visitors who perform a desired action on your website such as signing up for a free trial or filling out a form to download a lead magnet.
The conversion action doesn’t remain consistent across your website. The conversion rate, therefore, varies from page to page even on the same website. A high conversion rate is desirable as it indicates your SaaS site converts a high percentage of visitors into leads or customers.
11. Conversion Rate Optimization (CRO)
Used for: Improving the conversion rate of a website.
Conversion rate optimization is a systematic, scientific process to increase the conversion rate of a site. It involves tweaking different elements of a web page (e.g., headline, image, copy, CTA, form, colors, etc.), and then running A/B tests to find high-performing variation.
The process involves developing hypotheses, testing hypotheses, and running experiments in real time. CRO is an essential and continuous process where you keep changing your site to improve your conversion rate.
12. Cohort Analysis
Used for: Understanding customer behavior.
Cohort analysis helps you identify categories and groups in customer data. This grouping helps you track customer life cycle which makes it possible to calculate other SaaS terms and metrics such as retention rate, churn rate, etc.
The two common types of cohorts used by SaaS businesses include acquisition cohort (grouping based on sign-up date) and behavioral cohort (grouping based on customer actions such as completing a milestone).
13. Customer Journey Mapping
Used for: Understanding customer interactions with your brand end-to-end.
Customer journey mapping is a term that you’ll hear a lot as a SaaS founder. It is the process of creating a visual representation of all the customer interactions with your company. You can visually see the steps and paths customers take to move from one point to the next in their journey.
It helps you understand your customers, identify hurdles, and find opportunities.
14. Content Management System (CMS)
Used for: Managing digital content on your website.
Content management system is a software that helps you create, manage, and control digital content on your website in an entirely non-technical way. CMS allows you to create a website without any coding skills making it easy for anyone to create a website or manage a blog.
WordPress is the most popular open-source CMS that powers around 43.7% of global websites. It has a highly user-friendly interface that makes content management a piece of cake.
15. Cost Per Click (CPC)
Used for: Tracking cost per click for advertising campaigns.
Formula: Total ad spend / Total clicks
Benchmark: CPC depends on multiple factors including ad network, ad type, industry, targeting, and other variables. The average CPC for Google Search Ads across industries is $2.69 while it’s $0.63 for Google Display Network in 2024.
Cost per click is a bidding strategy used in the online advertising industry which means you pay for each click your ad receives. If your ad gets 100 clicks and the average CPC is $0.97, you will pay $97 for a total of 100 clicks.
The CPC pricing model is suitable for SaaS businesses that want to generate traffic irrespective of their conversion rate.
16. Cost Per Lead (CPL)
Used for: Measuring the cost of acquiring a lead or potential customer.
Formula: Total marketing spend / Total number of leads acquired
Benchmark: CPL can vary widely depending on the industry and target market, so it’s best to compare against your own historical data.
Cost per lead is a type of bidding strategy used in online advertisements such as Meta lead ads. It is a suitable pricing model for SaaS businesses that are looking to generate sign-ups and leads. The cost per lead model charges a fixed price for each lead generated regardless of the actual conversion rate.
17. Cost Per Mille (CPM)
Used for: Measuring the cost of displaying an ad to 1,000 impressions or views.
Formula: (Total advertising cost / Total number of impressions) x 1,000
Benchmark: CPM varies by industry, platform, targeting, and other factors. For instance, the average Google Ads CPM for technology was $6.40 and it was $1.95 for the government in 2024. It’s important to track your historical data and aim to optimize for better efficiency.
Cost per mile is a metric widely used in online advertising to evaluate the cost-effectiveness of ad campaigns. It is particularly beneficial for brand awareness campaigns that seek to maximize visibility rather than direct conversions. CPM ensures SaaS brands can assess the reach of their message while balancing their budget.
18. Call to Action (CTA)
Used for: Encouraging users to take a specific action after engaging with your content or ads.
A well-crafted call to action is essential for guiding users through the customer journey. CTAs play a pivotal role in converting prospects into customers whether it’s signing up for a free trial, downloading an ebook, or booking a software demo. Strategically placing and designing CTAs ensures users are motivated and directed toward the desired action that leads to a higher conversion rate.
19. Click Through Rate (CTR)
Used for: Measuring the effectiveness of a digital advertisement or link by calculating the percentage of users who click on it.
Formula: Clicks / Impressions x 100
Benchmark: A CTR above 2% is considered good for SaaS businesses. According to Google Ads data, the average CTR across all industries is 1.6%.
CTR is a critical indicator of how well marketing campaigns are capturing user interest. A higher CTR often translates to increased website traffic and subsequent conversions. High CTR means your ad copy is persuasive and is driving clicks.

20. Email Sending Platform (ESP)
Used for: Managing and delivering email marketing campaigns efficiently to a targeted audience.
Leveraging an ESP is essential for creating personalized and scalable email marketing campaigns. These platforms enable SaaS companies to reach and engage with their customers and subscribers effectively and keep them hooked.
Common examples of ESPs are Mailchimp, HubSpot, and Constant Contact. They offer features like A/B testing, email automation, and audience segmentation to optimize campaign performance.

21. Freemium
Used for: Offering a free version of a SaaS to attract users with optional paid upgrades for advanced features.
The freemium model is a widely used strategy in SaaS businesses to acquire new users. It focuses on providing a no-cost entry point so potential customers can explore your software. This model allows users to familiarize themselves with the product before deciding to invest in a premium plan.
Common benefits of the freemium model include increased brand exposure, a larger user base, and the opportunity to collect valuable user feedback.
22. Free Trial Conversion Rate
Used for: Measuring the percentage of free trial users who convert to paying customers.
Formula: (Number of paying customers / Number of free trial users) x 100
Benchmark: It depends on your industry, sales cycle, target audience, and other factors. Generally, 15% is considered a good free trial conversion rate for SaaS companies. B2B SaaS companies have a much lower rate as compared to B2C SaaS.
The free trial conversion rate is a crucial metric for SaaS businesses to track. It provides insights into how effectively your SaaS can convert free trial users into customers. A low conversion rate indicates an issue that needs to be found and addressed immediately to raise your rate and get back on track.
23. Feature Adoption
Used for: Measuring the percentage of users who actively use a specific feature of a SaaS product.
Formula: (Number of active users using the feature / Total number of active users) x 100
Benchmark: The average feature adoption rate for SaaS products is 6.4% and these 6.4% of features generate up to 80% of clicks. It is relative and depends on a lot of factors such as SaaS type, features, target audience, etc.
Tracking feature adoption can help SaaS companies identify which features are most popular among users and which ones may need improvement. It also informs decisions on future product development and marketing strategies. You should keep track of feature adoption and must take it seriously for your SaaS.

24. General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR)
Used for: Ensuring businesses comply with data protection and privacy laws when handling the personal data of individuals in the European Union.
Ensuring GDPR compliance is essential for maintaining user trust and avoiding hefty penalties. You must implement measures such as obtaining user consent, offering data portability, and providing tools for users to access, modify, or delete their data. Regular audits and updates to privacy policies are critical to staying compliant.

25. Horizontal SaaS
Used for: Providing solutions that serve a broad range of industries or businesses rather than focusing on a specific niche.
Horizontal SaaS products are designed to be versatile to meet the needs of users across diverse sectors. Examples include tools like customer relationship management (CRM) systems, email marketing platforms, or project management software. These apps prioritize scalability and can be customized to fit the requirements of almost all industries.
One major advantage of horizontal SaaS is its wide customer base and less reliance on a single market segment.

26. Inbound Marketing
Used for: Attracting customers through relevant and helpful content rather than intrusive ads.
Inbound marketing focuses on creating, publishing, distributing, and sharing valuable content to draw potential customers to your SaaS business. This approach typically involves publishing blog posts, social media marketing, search engine optimization (SEO), and other strategies that align with customer interests. The aim is to build long-term relationships by addressing users’ pain points and establishing trust.
27. Key Performance Indicator (KPI)
Used for: Measuring the performance and success of specific goals or objectives.
KPIs are quantifiable metrics that help your SaaS company track the progress of different goals such as marketing goals. Common examples include website traffic, conversion rates, and customer retention rates. You can identify areas for improvement and optimize your efforts for better results.
28. Landing Page
Used for: Capturing leads or driving a specific action from website visitors.
A landing page is a standalone marketing page designed to achieve a specific marketing objective such as encouraging visitors to sign up for a newsletter (lead generation) or buy a paid subscription to your SaaS (sale). It is optimized with compelling headlines, clear call-to-action, and minimal distractions to drive conversions.
29. Lead Magnet
Used for: Offering highly valuable freebies to potential customers in exchange for their contact information.
A lead magnet is an incentive used to entice prospects to share their email addresses or other details. For example, a free eBook, discount code, or free trial. This strategy helps your SaaS brand generate leads and build its email list and nurture leads effectively.
30. Lead Generation
Used for: Attracting and converting potential customers into leads.
Lead generation is the process of identifying and attracting potential customers to your SaaS business and converting them into leads. It involves marketing tactics like content creation, social media marketing, email marketing, PPC, etc. to capture and nurture prospects.
Landing pages, squeeze pages, and lead magnets are tools used for lead generation.
31. Lead Velocity Rate
Used for: Measuring the growth of qualified leads over time.
Formula: (New leads – Lost leads) / (Total number of leads at the beginning of the period) x 100
Benchmark: An LVR of over 5% is considered good while a rate of over 10% is excellent. However, it depends on numerous factors so it’s best to compare your lead velocity rate with your competitors to get a better idea of where you stand.
Lead Velocity Rate (LVR) is a metric used to track the growth of qualified leads at a specific time. It helps your SaaS company understand the effectiveness of its lead generation efforts and identify any issues in the lead nurturing processes.
32. Lead Scoring
Used for: Prioritizing and identifying high-value leads.
Lead scoring assigns a value to leads based on their behavior, engagement, characteristics, and other variables. This process helps sales and marketing teams focus their efforts on leads most likely to convert into customers.

33. Metric
Used for: Monitoring and measuring business performance.
A metric is a quantifiable measurement that SaaS businesses use to track and evaluate the success of specific processes, tasks, or strategies. Key metrics often include revenue, customer acquisition cost, sales, conversion rate, and website traffic.
34. Monthly Recurring Revenue (MRR)
Used for: Tracking predictable monthly revenue of a SaaS company.
Formula: Sum of all recurring revenue from active subscribers in a given month.
Benchmark: An MRR growth rate of 10% or more per month is considered good.
Monthly Recurring Revenue (MRR) is a key metric used by SaaS businesses to track and predict monthly revenue from their subscribers. It includes all recurring revenue from active customers in a given month including subscription fees, add-ons, and upgrades.
35. Monthly Active Users (MAU)
Used for: Evaluating SaaS engagement.
Formula: Total unique users who engage with the software within a month.
Benchmark: A steady MAU growth rate of 5-10% per month is considered healthy.
Monthly Active Users (MAU) represents the total number of unique users who interact with your SaaS app within a single month. It is a vital metric for understanding user activity and engagement over time.
36. Minimum Viable Product (MVP)
Used for: Testing product concepts with minimal resources.
A Minimum Viable Product (MVP) is the version of a product that allows your product and marketing teams to gather validated learning about customers with the least effort. It includes basic features to test market demand and get feedback for further development.
37. Marketing Qualified Lead (MQL)
Used for: Identifying leads ready for nurturing by sales.
Formula: Total leads x Qualification rate
Benchmark: An average MQL conversion rate ranges from 13% to 20% depending on the industry and lead generation strategies.
A Marketing Qualified Lead (MQL) is a lead that has shown interest in your SaaS product and its offerings through specific interactions such as downloading resources or attending a webinar. MQLs are passed onto sales for further engagement. MQL is a metric used by B2B SaaS companies with lengthy sales cycles where they have to connect with a potential client multiple times before conversion.

38. Net Promoter Score (NPS)
Used for: Measuring customer loyalty and satisfaction.
Formula: % Promoters – % Detractors
Benchmark: An NPS benchmark typically ranges from 30 to 50 where higher scores indicate strong customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Net Promoter Score (NPS) is a customer satisfaction benchmark that measures how likely customers are to recommend your company’s product or service to their friends and family. NPS is calculated through a single-item survey. It helps identify brand promoters and detractors.

39. Product-Led Growth
Used for: Driving growth through the product itself as the primary driver of customer acquisition and retention.
Product-led growth (PLG) is a business methodology where the product itself serves as the primary driver for customer acquisition, retention, and expansion. By focusing on delivering exceptional product experiences, SaaS companies enable users to derive value quickly which leads to organic growth.
40. Renewal Rate
Used for: Measuring the percentage of customers who renew their subscriptions at the end of a given period.
Formula: (Number of renewals ÷ Number of up-for-renewal customers) × 100
Benchmark: SaaS businesses typically aim for a renewal rate of 85% or higher. Enterprise SaaS companies should target 90% or higher.
Renewal rate is a critical metric for SaaS companies as it reflects the ability to retain existing customers. A high renewal rate indicates that customers find consistent value in your app which is essential for achieving long-term growth and stability.
41. Retention Rate
Used for: Evaluating the ability to retain customers over a specific period.
Formula: [(Number of customers at the end of the period – New customers acquired during the period) ÷ Number of customers at the start of the period] × 100
Benchmark: A healthy retention rate for SaaS companies is generally above 90% for enterprise customers and 75% for smaller businesses.
The retention rate reflects customer satisfaction and loyalty. It indicates the overall value they derive from the software. A high retention rate suggests that customers continue to find your app beneficial. It contributes to steady revenue and reduces the need for constant customer acquisition.
42. Return on Investment (ROI)
Used for: Measuring the profitability of an investment in a SaaS product or strategy.
Formula: (Net profit ÷ Investment cost) × 100
Benchmark: SaaS companies should target a positive and growing ROI. A high ROI indicates efficient expenditure and resource allocation.
ROI evaluates the efficiency and profitability of an investment (usually marketing) by comparing the net profit generated to the cost of the investment. It helps SaaS brands assess whether resources are being allocated effectively and ensures that spending contributes to sustainable business growth. A consistently positive ROI indicates successful financial management and strategic planning.
43. Return on Advertising Spend (ROAS)
Used for: Determining the revenue generated for every dollar spent on advertising.
Formula: Revenue attributable to ads ÷ Advertising spend
Benchmark: A ROAS of 3:1 or higher is considered healthy for SaaS businesses.
Return on Advertising Spend is a key performance metric for SaaS businesses to measure the effectiveness of their advertising efforts. It highlights how much revenue is generated for each dollar spent on ads. It provides insights into the profitability of marketing campaigns and reflects efficient customer acquisition and well-targeted ad strategies.

44. Sales Funnel
Used for: Visualizing and tracking the customer’s journey from awareness to purchase and beyond.
A SaaS sales funnel outlines the process potential customers go through before subscription. It typically includes stages such as attracting leads through marketing efforts, nurturing those leads with content, and converting them into paying customers. Each stage is designed to address specific customer needs and motivations with a focus on a smooth progression toward finalizing a sale.
45. Sales Qualified Lead (SQL)
Used for: Identifying leads that meet predefined sales criteria and are ready to engage with the sales team.
Formula: (Sales qualified lead ÷ Total leads) x 100
Benchmark: A conversion rate of 10-20% from MQL to SQL is common for SaaS businesses.
Sales Qualified Leads (SQL) are crucial for B2B SaaS businesses as they represent prospects who have shown significant interest and align with the ideal customer profile. These are the leads that have progressed beyond basic engagement and are ready for direct sales interaction.
46. Squeeze Page
Used for: Capturing a visitor’s contact information by offering a lead magnet.
A squeeze page is a standalone marketing page designed specifically to capture visitor information such as their name and email address in exchange for a valuable offer. This offer (known as a lead magnet) might include a free trial, demo, whitepaper, or an exclusive resource tailored to the SaaS audience.
47. Subscription Model
Used for: Generating recurring revenue through paid subscriptions.
The subscription model is a SaaS pricing strategy where customers pay a monthly or annual recurring fee to gain software access. This model fosters long-term customer relationships and provides SaaS businesses with a predictable revenue stream.

48. User Experience (UX)
Used for: Enhancing customer satisfaction and ease of use for SaaS products.
User Experience (UX) revolves around designing intuitive, efficient, and enjoyable interfaces that meet user needs. A good UX ensures that customers can easily navigate your app, complete tasks without friction, and derive value from the software.
49. Unique Visitors
Used for: Tracking the number of distinct users visiting a SaaS website over a specific time period.
Unique visitors refer to the total number of individual users who access your SaaS website during a specified period with each user being counted only once regardless of how many times they visit. This metric is crucial for understanding the reach of your SaaS website and gauging the effectiveness of marketing campaigns.
50. Upselling
Used for: Increasing revenue by encouraging existing customers to purchase premium features or higher-tier plans.
Upselling involves persuading existing SaaS customers to upgrade to a higher-tier plan or purchase additional features. It focuses on enhancing customer lifetime value by increasing revenue per customer.
A strong upselling strategy can contribute to a 30-50% increase in overall revenue for SaaS companies.
51. User Onboarding
Used for: Guiding new users through initial steps to experience the value of a SaaS product quickly.
User onboarding is the process of introducing new users to your SaaS and ensuring they understand its features and benefits. It aims to help new users achieve desired outcomes as quickly as possible.
It is a positive first impression aimed at increasing the likelihood of long-term engagement. The onboarding process includes tutorials, walkthroughs, and helpful prompts tailored to the user’s specific needs.

52. Vertical SaaS
Used for: Building a specialized SaaS product tailored to a specific industry or niche.
Vertical SaaS focuses on addressing the unique needs of specific industries by providing tailored solutions that cater to niche markets. Unlike horizontal SaaS, which serves a broad range of industries, vertical SaaS delivers industry-specific functionalities. This results in higher customer satisfaction and stronger market positioning within the chosen sector.
Vertical SaaS businesses have higher retention rates and loyalty compared to horizontal SaaS.
Final Words
A clear understanding of common SaaS marketing terms, terminologies, definitions, and acronyms is essential for SaaS founders and marketing teams. It lets you understand marketing, get better at decision-making, and figure out bugs and loopholes quickly.
Need help with your SaaS marketing?
You can get in touch with us and see how we can help you grow your SaaS brand organically.